NFS Service
Web Ten includes NFS capabilities that allow it to mount NFS volumes from any NFS server. This means that enterprise-wide or campus-wide workstations, minis or mainframes can easily be used to store Web Ten content. These volumes can then be published within the content hierarchy of the Web Ten Web server. The NFS servers can contain the Web pages for an entire Web site, a set of specific virtual hosts, or simply a component of a virtual host.
The Web Ten NFS client service is compatible with any NFS server implementation. Support for read-only access to the NFS volumes is also provided.
Configuring the NFS Server
An NFS server typically requires some configuration to specify which NFS clients are permitted to mount its volumes. For example, an NFS server typically needs to be configured with a host name or IP address for each such client. To permit a Web Ten system to mount any of its volumes, the server typically needs to have the host name or IP address of the Web Ten systems entered into its NFS configuration database. Each type of NFS server has its own configuration database and instructions. You should review the documentation for that system or consult the system administrator for that system before attempting to mount any NFS system from within Web Ten .
NFS User and Group Numbers
When an NFS request is sent from an NFS client to an NFS server, user and group identification numbers are included in the request. These numbers are used by the server to determine what type of access is to be permitted for that specific request. NFS servers can selectively permit or deny access for the reading or writing of any file and the indexing of any directories.
Web Ten systems use the user ID 65534 ( nobody -2 ) and the group ID 65535 ( nogroup -1 ) for all NFS requests. These IDs are configured in the httpd.conf configuration file.
Web Ten systems use the user ID 65533 and the group ID 65533 for all anonymous FTP requests passed to the NFS server. All other password-based FTP requests use the user ID 1000 and the group ID 100.
NFS Settings
The NFS Settings table contains options that control Web Ten NFS capabilities. The NFS capabilities are an integrated component of Web Ten and are designed to provide NFS access points (within the Web server's content hierarchy) to NFS server systems. The NFS access points can be based on complete virtual host content trees, or they can be sub-folders within a virtual host's content tree. The NFS access points can also be restricted to read-only access from the NFS server. This protects the NFS server from any modifications attempted via a CGI or a plug-in that is executed on the Web server.
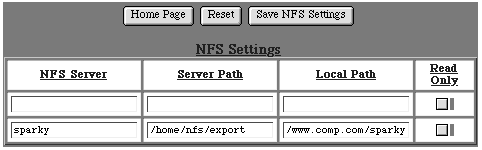
NFS Server
The NFS Server is the name of the system on which the NFS volume actually resides. This name may be a fully qualified domain name or a partially qualified domain name within the same domain as the Web Ten system. Alternatively, an IP address in dot notation may be used if Web Ten cannot resolve (via DNS) the name of the NFS server.
Server Path
The Server Path is the path to the desired folder or directory on the NFS server. The NFS server uses this path to identify the top or highest level directory that will be exported to Web Ten .